After the last two posts Yuan Devaluation: Currency Wars Revisited and Yuan devaluation: currency wars (part 2), we are ready to tackle the current situation in the currency wars space.
As you recall from the past posts, the western world suffered a lot due to the competitive currency devaluations. You would think that the countries involved in the first currency battles understood that devaluation or depreciation (you know the difference now) was not the way of growth, and that it would result in a lose lose situation for all the parties involved. Well, the issue is that a new player came into the battlefield, please welcome…. China!
The World Bank web has an amazing database (seriously); you can find almost anything in there! I searched for the growth rates of Chinese exports since the Chinese economic reforms from 1978 started to bear fruits, and its quite stunning to see the numbers (you can check a really cool timeline from the CSIS about the Chinese reforms).
From 1983 up to 1993 the growth rate on the exports coming from China was, in average, 9.72%, already higher than the one from the U.S., 7.35%. The impact of the economic measurements started in December 1978 and led by Deng Xiaoping was noticeable, however, there was something else going on. During this period the Yuan dropped its value from an overvalued position of around 2.8 Yuan per dollar to one of 5.32 Yuan per dollar.
Up to that point, the U.S. was not complaining that much (only a bit) about these devaluations. At one point, in January 2004, the Chinese government went too far, at least in the eyes of the U.S. authorities, and devalued the Yuan to a rate of 8.7 Yuan per dollar. At this point the U.S. Treasury cried that China was a “currency manipulator,” and stated that the exchange levels were set at a point significantly different from the one that they would have been if no actions were taken by the Chinese authorities.
The Treasury had voiced before its concerns and stated that the Chinese government was manipulating its currency, however, this time raised its voice louder. This might be the reason why from this point China didn’t devalue more its currency. From 1994 until 2004 the exports from China grew at a rate of 17.5%, while the U.S. exports grew at 5.2%. The trade imbalance between the two countries in 1985 was almost 0 ($6 billion in favor of China), which means that China imported, almost, as much as it exported to the U.S. In 2004 the trade imbalance was over $162 billion in favor of China (and it would continue growing, in 2014 it was $592 billion).
In the meantime the Yuan was revalued from 8.7 to 8.28 Yuan per euro (during the period 1994 to 1997, and it stayed pegged from 1997 at the rate of 8.28)… What a change!
The currency policy that China kept by pegging the Yuan to the U.S. dollar at a fixed rate is the type of policy that developing economies use in order to protect their currency from volatility. However, this peg was not adjusted accordingly in light of the change in the economic developments on both countries that would have caused the Chinese currency appreciate against the dollar.
As a side note I believe is important to note that Japan has been categorized as a currency manipulator by some international leaders such as Angela Merkel. Since I want to focus in the Chinese situation I encourage you to do some research into these allegations.
Due to the international pressure, or maybe due to something that I don’t really know about, in 2005 the PBC decided to end the peg to the dollar and swap it with a rate that would be adjustable to the movements of a currency basket in which the dominant ones are the USD, EUR, JPY, and KRW. The adjustments would be based on market supply and demand but made at the discretion of the central bank of china.
After the measurement was enforced the Yuan appreciated, though slowly, from 8.28 to 6.83 Yuan per dollar in 2008. The type of currency system that China was experimenting with was considered a true managed float, since, despite of the market forces determining the value of the currency, the monetary authorities were able to modify the rate at which the currency could appreciate or depreciate by the means of market intervention.
As you can see, China allowed the Yuan to appreciate almost 21%, showing that the country was ready to have a more important role in the global financial world.
Due to the slowdown in global demand for Chinese products on the back of the financial crisis, China decided to fix again its rate at 6.83 Yuan per dollar in 2008.
However, it decided to give on to the international pressures quite fast, especially coming from the U.S., and in 2010 it resumed its currency liberalization again. The PBC stated in June 2010 that they would avoid any sharp appreciation of the Yuan, but that they would keep small and consistent appreciations. From 2010 to 2013 the Yuan appreciated from 6.83 to 6.17 Yuan per dollar.
There is a “rumor” going on that during this period the Chinese were timing the appreciations in advance of international summits to keep the mood up during these summits. There might be some truth in these statements.
To tell you the truth, I am not completely sure that these three posts have a proper title…
It was pointed out to me in a comment to the first post in the series (link on top) that it should be currency depreciation and not devaluation. In that moment I was pretty sure that it was not a depreciation but a devaluation, since it was clearly a direct intervention from the Chinese monetary authorities, but now, after thinking more about the topic and understanding how hard it is to find the true value of the Yuan I am not completely sure. But let me explain what this last depreci/devalu-ation is all about.
From my perspective there are two major groups (in the way experts are reacting):
The first group:
This group of experts believes that China is just letting its currency depreciate against the basket that the Yuan is compared to. Since the basket contains dollars, and the dollar has been so strong, every other currency in the basket has depreciated against it. The Chinese Yuan is relatively overvalued in terms of this last currency move that started a little over a year ago. Hence, the move its not really a devaluation but a depreciation.
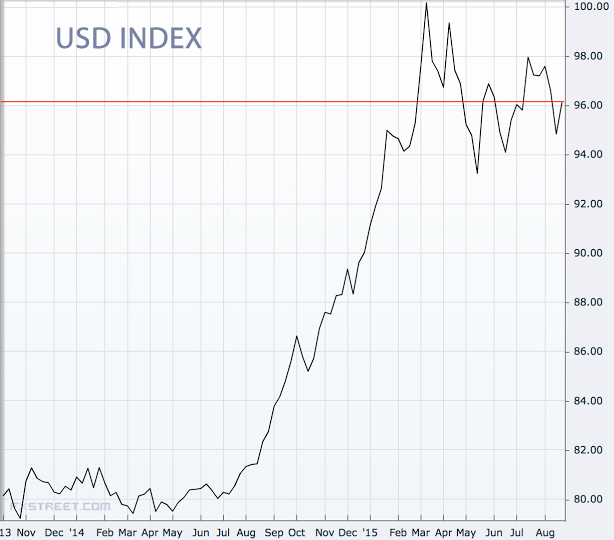
This group would say that the move was necessary because, for example, the euro had dropped over 15% against the dollar while the Yuan remained unchanged. When we think about the fact that Europe is the largest trade partner of China we can see a problem here.The second group
The second group:
The second group believes that in order for the move to be consider a depreciation instead of a devaluation, first the Yuan should have been at a fair value vis a vis the dollar. What this second group thinks is that the Chinese authorities are starting to fear that the forecasted GDP growth rate will fall even more and China is trying to boost it by manipulating the exchange rate in order to boost exports.
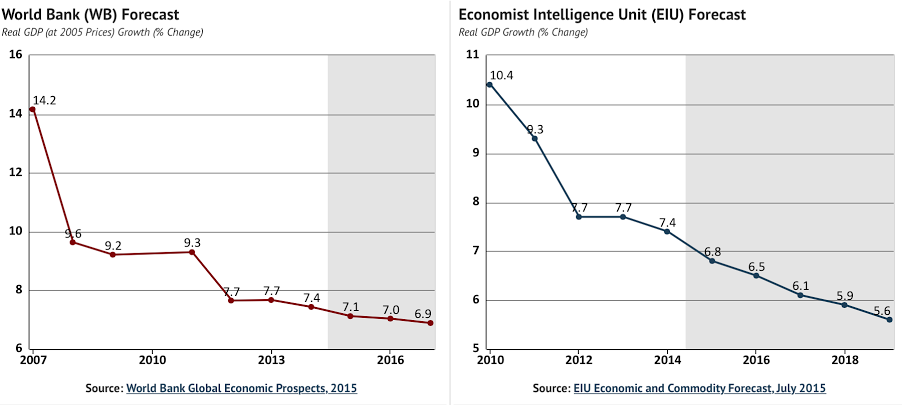
If this ends up being the case, the global economy will suffer. Because if this is the case, this is not the end of the Yuan devaluation, a series of larger devaluations will come and the economic unrest will become fear.
Some of the already observed consequences
We are seeing quite a few Asian currencies are now under pressure due to this move by the PBC, but the most affected for now have been the Indonesian Rupiah and the Malaysian Ringgit.
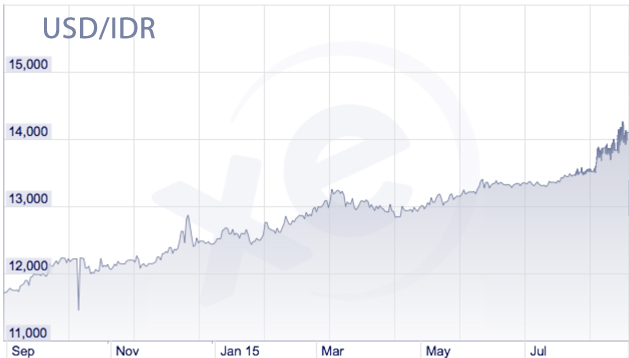
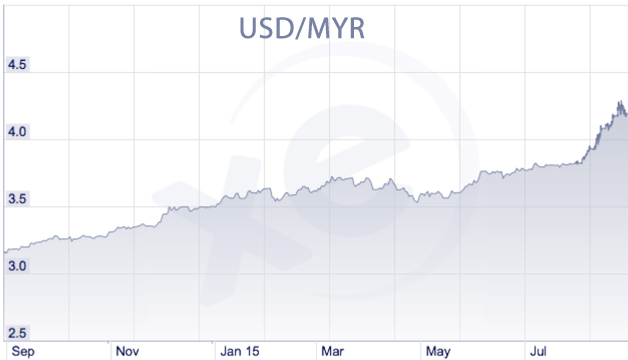
As some market participants are part of the second group, we saw some moves in the markets, and volatility spiking up.
I would like to recommend a reading in one of the most interesting blogs in finance: Zero Hedge. “It’s Official: China Confirms It Has Begun Liquidating Treasuries, Warns Washington.” In the post, “Tyler Durden” explains how after the recent devaluation “China has likely sold somewhere on the order of $100 billion in US Treasuries in the past two weeks alone in open FX ops to steady the Yuan.” The read requires a bit of deeper knowledge than our reads, but I think that after reading the past 3 posts on Currency Devaluation all of you can understand the points that the post makes.
The truth is that we will not know with certainty what the true motives of the Chinese governments are until a few more months, so for now we have to remain expectant!
Source: source: Opseeker – Contributing to financial literacy
Dig deeper
Mis en ligne le 01/08/2014 ![]() pratclif.com
pratclif.com